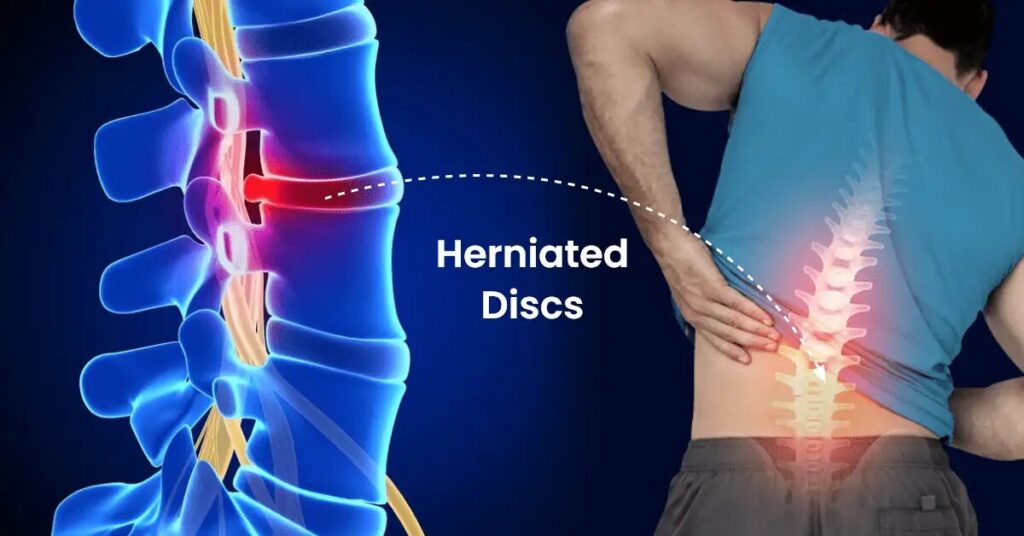
Disc Bulge and Herniation
📌 What is a Disc Bulge?
A disc bulge occurs when an intervertebral disc extends beyond its normal boundary in the spine. This condition can cause discomfort, stiffness, and in severe cases, nerve compression leading to pain, weakness, or numbness.
While often referred to as a slipped disc, the term is misleading. Spinal discs do not slip; rather, they bulge or herniate due to various factors.
⚠️ Common Causes of a Bulging Disc
Several factors contribute to the development of a disc bulge, including:
✔️ Aging – As we grow older, spinal discs lose water content, becoming more brittle and prone to damage.
✔️ Injury & Trauma – Accidents, falls, or improper lifting techniques can put excessive strain on the spine.
✔️ Poor Posture – Sitting for long periods with bad posture can increase pressure on the spinal discs.
✔️ Repetitive Movements – Jobs or activities that involve constant bending, twisting, or heavy lifting can accelerate disc wear and tear.
✔️ Obesity – Excess body weight puts additional stress on the spine, increasing the risk of a bulging disc.
🔍 Disc Bulge vs. Herniated Disc
A bulging disc and a herniated disc are related but distinct conditions:
✅ Bulging Disc – The disc protrudes outward but remains intact, putting pressure on nearby nerves.
✅ Herniated Disc – The outer disc layer tears, allowing the inner gel-like material to leak out, often causing inflammation and severe nerve pain.
❗ Symptoms of a Bulging Disc
The symptoms of a disc bulge vary depending on its location in the spine:
🟢 Neck (Cervical Spine)
- Pain in the neck, shoulders, or arms
- Numbness or tingling in hands and fingers
- Headaches or dizziness
🟠 Lower Back (Lumbar Spine)
- Lower back pain, especially after sitting or standing for long periods
- Sciatica – pain radiating down one or both legs
- Weakness in the legs or difficulty walking
🔴 Middle Back (Thoracic Spine) (Less common)
- Pain around the ribs and chest
- Stiffness in the mid-back area
💡 When to Seek Medical Help?
If you experience:
⚡ Severe pain that doesn’t improve with rest
⚡ Loss of bladder or bowel control (a medical emergency)
⚡ Sudden weakness in arms or legs
⚡ Numbness in the inner thighs or saddle region
Consult a specialist immediately for evaluation and treatment.
🏥 Treatment Options for a Disc Bulge
The good news is that most cases of a bulging disc can be treated without surgery.
🌿 Non-Surgical Treatments
✔️ Rest & Activity Modification – Avoid heavy lifting and activities that worsen pain.
✔️ Physical Therapy – Exercises to strengthen core muscles and improve flexibility.
✔️ Chiropractic Care – Gentle spinal adjustments to reduce nerve pressure.
✔️ Massage Therapy – Helps relieve muscle tension around the affected disc.
✔️ Pain Relief Medications – NSAIDs or muscle relaxants to ease inflammation.
🔬 Advanced Treatments
If symptoms persist, doctors may recommend:
💉 Epidural Steroid Injections – Reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief.
⚡ Spinal Decompression Therapy – A non-surgical technique to relieve disc pressure.
🔪 Surgery (Last Resort) – Procedures like discectomy or spinal fusion may be needed in severe cases.
✅ Preventing a Bulging Disc
Protect your spine by adopting healthy habits:
🏋️ Stay Active – Regular exercise strengthens the muscles supporting the spine.
🪑 Maintain Good Posture – Keep your back straight while sitting or standing.
📏 Lift Correctly – Bend your knees, not your back, when picking up heavy objects.
🍎 Eat a Healthy Diet – Proper nutrition keeps spinal discs hydrated and strong.
💤 Use Supportive Bedding – A good mattress and pillow help maintain spinal alignment.
🏆 Take Control of Your Spinal Health
A disc bulge doesn’t have to control your life. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, you can manage symptoms effectively and prevent further damage.